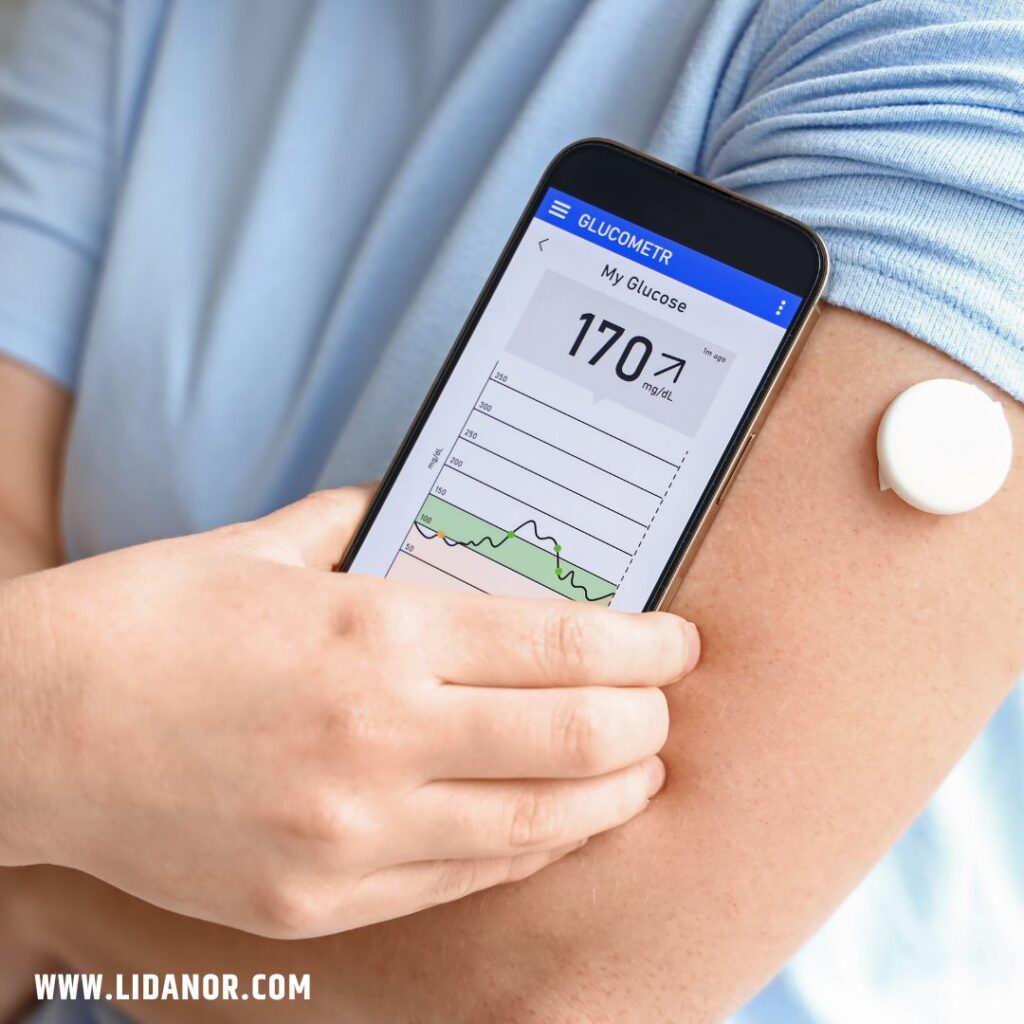
Glucose, often referred to as “blood sugar,” might sound simple, but it’s the lifeblood of our cellular energy. It’s a simple sugar, the primary fuel source for most of our body’s functions, and understanding its role is crucial for maintaining good health.
Glucose: The Powerhouse Molecule
Our bodies obtain glucose from the carbohydrates we consume. When we eat, complex carbohydrates like starches and sugars break down into glucose molecules in our digestive system. This glucose then enters the bloodstream through the small intestine, ready to be delivered to its cellular destinations.
How Does Glucose Get Used?
Every cell in our body craves glucose, but some are more dependent on it than others. Here’s where it gets interesting:
- The Brain’s Fuel: Our brain is a massive consumer of glucose, requiring a steady supply for optimal cognitive function, focus, and memory.
- Muscles in Motion: During physical activity, our muscles rely heavily on glucose for immediate energy. When glucose stores are depleted, fatigue sets in.
- Energy for All: Even organs like the heart, kidneys, and liver utilize glucose for essential functions.
Maintaining Balance: The Role of Insulin
So how does our body ensure a constant supply of glucose for our cells? Here’s where another key player comes in – insulin. This hormone, produced by the pancreas, acts like a key, unlocking the doors of our cells and allowing glucose to enter.
Glucose Levels: A Delicate Dance
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial. Ideally, glucose levels should remain within a specific range. When levels are too high (hyperglycemia), it can lead to health problems like diabetes. Conversely, if levels drop too low (hypoglycemia), fatigue, dizziness, and even seizures can occur.
Understanding Glucose and Managing It for Life
Whether you’re concerned about maintaining optimal health, managing diabetes, or simply want to understand your body’s energy source better, here are some key takeaways:
- Focus on Complex Carbs: Choose whole grains, fruits, and vegetables over refined sugars and processed foods. These provide a sustained release of glucose, keeping your energy levels stable.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps your body utilize glucose more efficiently, promoting healthy blood sugar levels.
- Monitor Your Blood Sugar: If you have diabetes or are concerned about your blood sugar levels, talk to your doctor about monitoring options.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: A doctor or registered dietitian can create a personalized plan to manage your glucose levels and optimize your overall health.
The Future of Glucose Research
Scientists are constantly striving to understand glucose metabolism better. Research is ongoing in areas like:
- Precision Nutrition: Tailoring dietary recommendations based on an individual’s response to different types of carbohydrates.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring: New technologies for real-time blood sugar monitoring and management.
- Diabetes Prevention and Treatment: Developing new strategies to manage and potentially prevent diabetes.
Conclusion:
Glucose, the simple sugar with a complex story, is the fuel that keeps our bodies running. By understanding its role and making healthy choices, we can optimize our energy levels, maintain good health, and live a vibrant life.